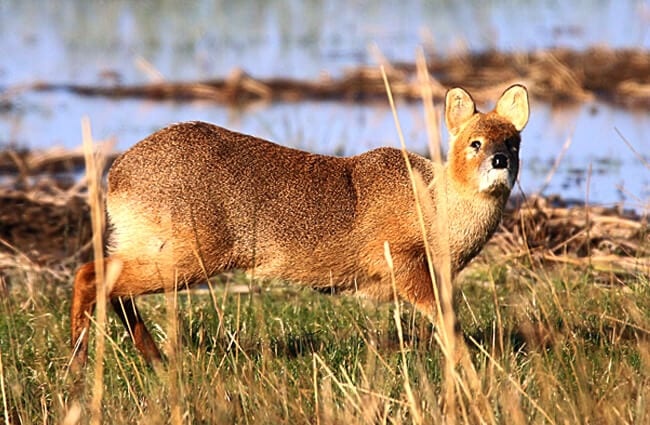
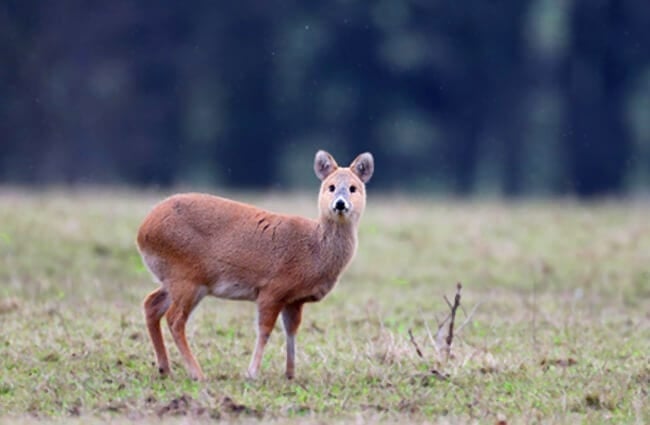
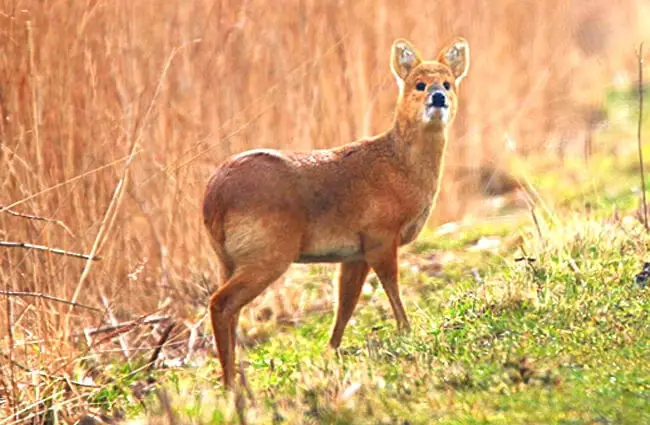
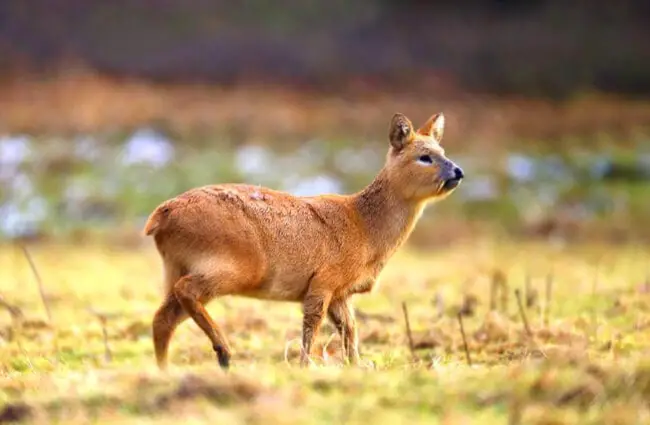
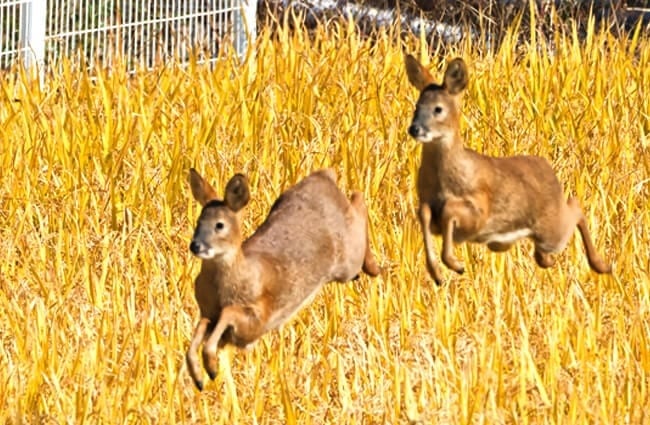
Water Deer are small, unique little deer that live in China and Korea. They are part of the Cervidae family, along with other deer, elk, moose, and more. This species does not grow antlers, and has abnormally long canine teeth.
There are two different subspecies of Water Deer, Chinese Water Deer and Korean Water Deer. Read on to learn about the Water Deer.
Description of the Water Deer
This species of cervid is quite small. They only stand 18 – 22 in. tall at the shoulder, and are no larger then 3.3 ft. long. Their weight averages around 20 or 30 lbs. at the most.
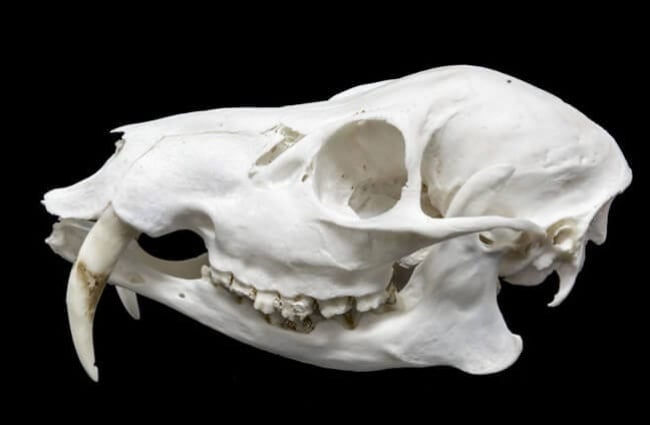
These deer have golden brown coats and white underbellies. Their rear legs are also noticeably longer than their front legs. Water deer also the lack antlers that most other deer species posses. However, they do have something most deer lack… tusks!
Interesting Facts About the Water Deer
You can tell that Water Deer are unique just by looking at them. Their long “tusks” and lack of antlers truly differentiate them from many other species of deer. Learn more the unique dentition of this species below.
- Strange Nickname – Water deer have a rather odd nickname. In some areas, people call Water Deer “vampire deer.” This strange nickname is a reference to their long tusks.
- Deer Tusks – Water deer tusks are actually elongated canine teeth. These extensively overgrown canines grow up to 3.2 in. long in some animals! Males have longer tusks than females.
- Tusk Purpose – Despite their vampiric nickname, Water Deer do not use their long teeth to suck blood. Like all deer, Water Deer are herbivores. Instead, this species uses its long tusks to fight rival males for the right to breed with females.
Habitat of the Chinese Water Deer
These deer are particularly fond of water plants, and watery areas, like swamps. In addition to swampy habitats, Water Deer live in grasslands, mountainous regions, along rivers, and more.
Water deer also live in agricultural areas and inhabit cultivated fields. While they seem to like water, they do prefer dry land when they are not feeding.
Distribution of the Water Deer
The Water Deer’s natural range is Asia, specifically China and Korea. The two subspecies live in the respective countries of their namesake, China and Korea.
In China, they live primarily in the basin of the Yangtze River in Central China. In addition to their natural range, humans have also introduced this species to England and France.
Diet of the Water Deer
Water deer, like the vast majority of cervids, are herbivores. Their favorite foods are a variety of aquatic vegetation. Much of their diet consists of reeds, beets, and fresh shoots of grass.
Unlike some other species of deer, Chinese Water Deer are actually very picky eaters. They cannot digest dense vegetation as well as other species, and because of this they choose plants that are less fibrous with higher protein and fat.
Water Deer and Human Interaction
Sadly, conflict with humans is not uncommon for this species. Humans hunt the deer extensively, for both meat and colostrum milk. The female deer create colostrum for only a few days after giving birth.
Hunters sell the colostrum to those who use it in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Humans also kill the deer for eating their crops. Because of these threats, the IUCN lists Water Deer as Vulnerable.
Domestication
Humans have not domesticated Water Deer in any way.
Does the Water Deer Make a Good Pet
No, Water Deer do not make good pets. They are wild animals, and their tusks are quite sharp. Because of this, they can be relatively dangerous when threatened or cornered, making them a poor choice as a pet.
Water Deer Care
Because these deer are so small, they do not require immense enclosures sometimes needed for other members of the Cervidae family. Instead, various hiding places are more important, as well as a variety of grasses and plants to browse on.
Their diet is more particular than many other species as well. Zookeepers feed them pelleted food, different types of fruits and vegetables, hay, and freshly trimmed plants.
Behavior of the Water Deer
Following the “different from other deer trend,” Water Deer do not live in herds. Instead, they usually live in pairs, or alone. They are shy creatures, and use dense vegetation and quiet movement to hide from potential threats.
Males, called “bucks,” are highly territorial, and will fight other males if they enter their territory. Despite this, bucks do allow females in their territory, and they will mate with them when they are receptive.
Reproduction of the Water Deer
Female Water Deer are usually receptive between November and January. After mating, the gestation period is around 6 months long, though it varies by individual.
This species gives birth to 2 – 3 babies, called “calves.” However, they can produce as many as 6 – 8 calves in a single birth. The young deer nurse for several months before their mother weans them off her milk.











![Red Angus Closeup of a beautiful Red Angus cowPhoto by: U.S. Department of Agriculture [pubic domain]https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/](https://animals.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/Red-Angus-4-238x178.jpg)












![Red Angus Closeup of a beautiful Red Angus cowPhoto by: U.S. Department of Agriculture [pubic domain]https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/](https://animals.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/Red-Angus-4-100x75.jpg)

