Beneath the shimmering surface of the Atlantic and Gulf coasts, a true culinary and ecological marvel glides through the surf. Known for its exquisite flavor and spirited fight, the Florida Pompano (Trachinotus carolinus) is far more than just a prized catch. This remarkable fish holds a vital place in marine ecosystems and offers a fascinating study for anyone intrigued by the ocean’s biodiversity.
From its distinctive appearance to its intricate life cycle, the Florida Pompano embodies the dynamic beauty of coastal waters. Join us as we dive into the world of this silvery speedster, uncovering its secrets and appreciating its profound impact.
Meet the Florida Pompano: A Coastal Gem
The Florida Pompano is a member of the jack family (Carangidae), a group known for its fast-swimming, often predatory marine fish. It is easily recognized by its deep, compressed body, which gives it a somewhat oval profile. Its coloration is typically silvery, often with a hint of gold or yellow on its belly and fins, particularly the pelvic and anal fins. The mouth is small, and its body lacks the scutes (bony plates) found on many of its jack relatives, giving it a smooth, streamlined appearance.
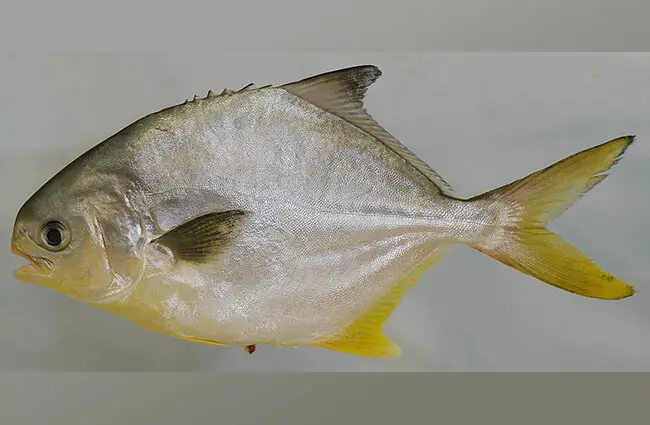

Where They Call Home: Habitat and Range
Florida Pompano are true inhabitants of the surf zone, preferring sandy beaches, shallow coastal waters, and the mouths of estuaries and bays. They thrive in warm temperate to tropical environments. Their geographical range is extensive, primarily along the Atlantic coast of the United States, stretching from Massachusetts down to Florida, and throughout the Gulf of Mexico. They are also found in the Caribbean Sea and along the coast of Brazil.
These fish are often found near oyster beds, seagrass flats, and other structures that provide food and shelter, though their preference for sandy bottoms is paramount. They are highly migratory, moving north into cooler waters during the warmer months and retreating south to warmer climes as winter approaches.
What’s on the Menu: Diet and Foraging
As opportunistic carnivores, Florida Pompano are primarily bottom feeders. Their small, downturned mouths are perfectly adapted for rooting around in the sand for buried prey. Their diet consists mainly of small crustaceans, such as shrimp, crabs, amphipods, and copepods. They also consume mollusks, particularly coquina clams and sand fleas, which are abundant in their preferred surf zone habitat. Marine worms and occasionally small fish round out their varied diet.
The Circle of Life: Reproduction and Growth
The life cycle of the Florida Pompano begins with spawning events that typically occur offshore. Females release large numbers of pelagic (free-floating) eggs, which are then fertilized externally by males. These eggs drift with the currents, eventually hatching into tiny larvae. The larvae then make their way to inshore nursery grounds, such as estuaries and protected surf zones, where they can feed and grow relatively safely from larger predators.
Pompano grow rapidly, reaching sexual maturity around one year of age. They can live for several years, with larger individuals reaching lengths of up to 25 inches and weights of over 8 pounds, though most commonly encountered specimens are between 1 to 3 pounds.
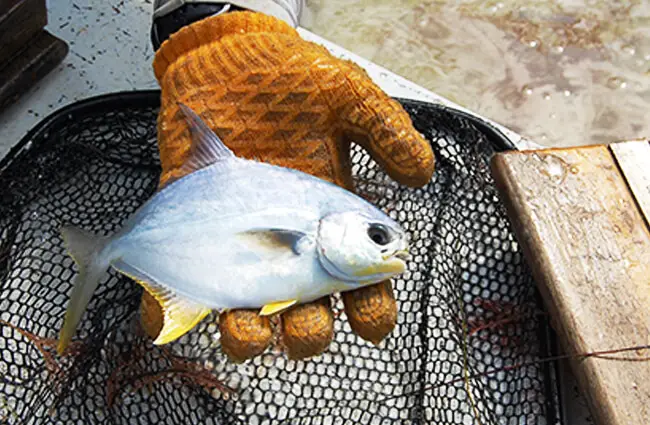

A Deeper Dive: Unraveling Pompano Ecology and Evolution
For the aspiring zoologist or dedicated researcher, the Florida Pompano offers a wealth of fascinating insights into marine biology.
Evolutionary History: A Glimpse into the Past
The Florida Pompano belongs to the Carangidae family, a diverse group of fish that includes jacks, trevallies, and scads. This family has a long evolutionary history, with fossil records indicating their presence in ancient oceans. Carangids are characterized by their streamlined bodies, forked tails, and often silvery coloration, adaptations that speak to their active, predatory lifestyle in open water and coastal environments. The Pompano’s specific adaptations, such as its small mouth and bottom-feeding habits, represent a specialized niche within this broader family, allowing it to thrive in the dynamic surf zone.
Ecological Contributions and Interactions
Florida Pompano play a crucial role in the coastal food web. As predators of various invertebrates, they help regulate populations of crustaceans and mollusks, preventing any single species from dominating their habitat. In turn, pompano themselves serve as an important food source for a variety of larger marine predators. Sharks, barracuda, larger predatory fish, and even seabirds will prey on pompano, especially juveniles in shallow waters. Their migratory patterns also contribute to nutrient cycling and energy transfer across different coastal ecosystems.
Reproductive Strategies and Larval Development
The reproductive success of the Florida Pompano is tied to its ability to produce multiple batches of eggs over an extended spawning season, which can last from spring through fall in warmer regions. This serial spawning strategy increases the chances of some larvae encountering favorable conditions for survival. The pelagic eggs and larvae are highly susceptible to environmental factors such as temperature, salinity, and current patterns. The journey of the larvae from offshore spawning grounds to inshore nursery areas is a critical and perilous stage, with only a small fraction surviving to adulthood. These nursery habitats, often estuaries and protected surf zones, provide abundant food and some refuge from predators, highlighting the importance of conserving these vital coastal areas.
Human Interaction and Cultural Significance
The Florida Pompano holds significant value for humans, both economically and culturally.
- Commercial Fishery: It is one of the most highly prized food fish in the southeastern United States. Its firm, white, delicate-flavored flesh is considered a gourmet item, fetching high prices in markets and restaurants. Commercial fishing operations target pompano using various methods, including gillnets and seines.
- Recreational Fishing: Pompano are a favorite target for recreational anglers, particularly surf fishermen. Their strong fighting spirit and delicious taste make them a rewarding catch. Anglers often use specialized rigs with small jigs or natural baits like sand fleas and shrimp.
- Aquaculture Potential: Due to its high market value and rapid growth rate, the Florida Pompano has been identified as a prime candidate for aquaculture. Research and development in pompano farming aim to meet consumer demand while potentially reducing pressure on wild stocks.
- Culinary Heritage: In coastal communities, particularly in Florida, pompano is deeply embedded in local culinary traditions. Recipes featuring baked, broiled, or pan-fried pompano are staples, celebrating its unique flavor.
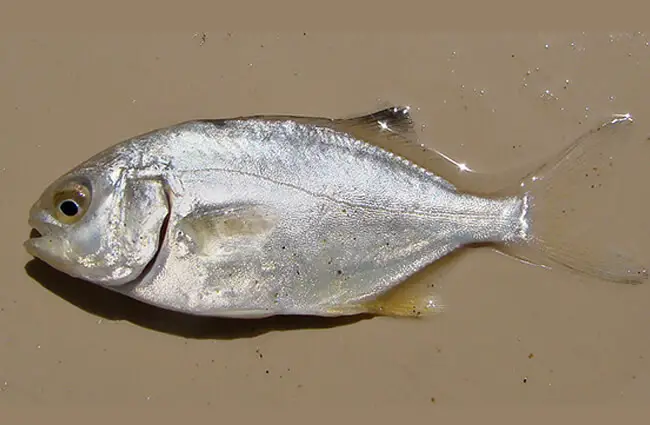

Practical Insights: Finding, Observing, and Caring for Pompano
Whether you are an animal lover, an aspiring zoologist, a hiker by the sea, or a zookeeper, understanding how to interact with Florida Pompano is key.
Finding Florida Pompano in the Wild
For those hoping to observe Florida Pompano in their natural habitat, the key is to visit their preferred environments during the right season.
- Location: Focus on sandy beaches, especially those with a moderate surf. Look for areas where waves are breaking, creating a turbulent zone. Estuary mouths and shallow bays with sandy bottoms are also prime locations.
- Time of Year: In Florida and the Gulf Coast, pompano can be found year-round, but their numbers swell during spring and fall migrations. Further north, summer is the best time.
- Time of Day: Pompano are often active feeders during dawn and dusk, but can be found throughout the day, especially on incoming or outgoing tides.
- Observation Tips: While they are fast-moving fish, keen observers might spot them darting through clear, shallow water, especially near sandbars or troughs. Look for subtle disturbances in the water or flashes of silver. Snorkeling in clear, shallow surf zones can sometimes offer glimpses.
Encountering Florida Pompano: What to Do
If you are a hiker or beachgoer and happen to spot a Florida Pompano in the wild, the best approach is one of respectful observation.
- Maintain Distance: Like all wild animals, pompano should be observed from a distance to avoid disturbing their natural behavior.
- Do Not Interfere: Avoid attempting to touch, feed, or interact with the fish. If a pompano appears stranded or distressed, contact local wildlife authorities or marine rescue organizations rather than attempting a rescue yourself.
- Appreciate the Moment: Take a moment to appreciate the beauty and agility of this coastal resident. It is a rare treat to witness such a prized fish in its natural element.
Caring for Florida Pompano in Captivity: A Zookeeper’s Guide
Caring for Florida Pompano in an aquarium or aquaculture setting requires specific knowledge of their environmental and dietary needs.
- Tank Requirements:
- Space: Pompano are active swimmers and require large tanks with ample open swimming space.
- Water Quality: Pristine water quality is paramount. Maintain stable salinity (typically marine, around 30-35 ppt), temperature (ideally 70-80°F or 21-27°C), and pH (7.8-8.4). Robust filtration systems are essential to handle their waste.
- Substrate: A sandy substrate is beneficial, as it mimics their natural foraging environment and allows them to exhibit natural digging behaviors.
- Water Flow: Moderate to strong water flow is appreciated, simulating their surf zone habitat.
- Diet:
- Variety: Offer a varied diet of high-quality marine pellets, frozen or live brine shrimp, mysis shrimp, chopped squid, and small pieces of fish.
- Frequency: Juveniles may require multiple feedings per day, while adults can be fed once or twice daily.
- Foraging: Encourage natural foraging by scattering food on the sandy bottom.
- Social Behavior: Pompano are schooling fish and generally do well in groups. However, monitor for any signs of aggression, especially during feeding.
- Health Monitoring: Regularly observe for signs of stress or disease, such as lethargy, clamped fins, lesions, or abnormal swimming patterns. Quarantine new arrivals to prevent disease introduction.
- What to Avoid:
- Overcrowding: This leads to stress, poor water quality, and increased disease susceptibility.
- Sudden Changes: Avoid abrupt changes in water parameters, as pompano are sensitive to environmental shifts.
- Incompatible Tank Mates: Do not house with overly aggressive or very small, delicate fish that could be prey.
- Poor Nutrition: A monotonous or low-quality diet can lead to nutritional deficiencies and health problems.
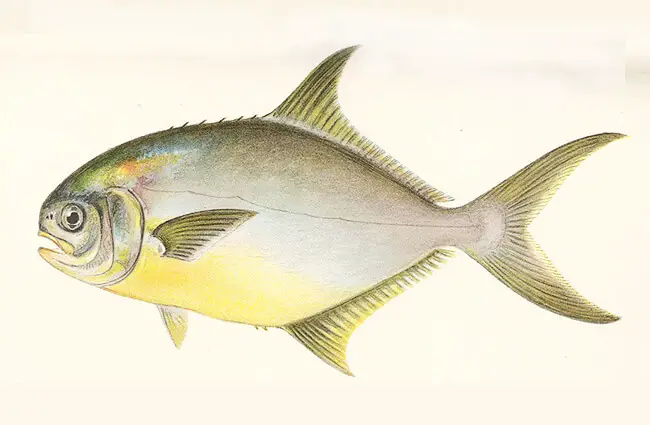
Interesting Facts About Florida Pompano
- The Florida Pompano is often considered one of the finest eating fish in the world due to its delicate, sweet flavor and firm, white flesh.
- Despite its name, Florida Pompano are found far beyond Florida, ranging up the Atlantic coast and throughout the Gulf of Mexico.
- They are known for their strong, acrobatic fights when hooked, making them a favorite among sport fishermen.
- Pompano lack scutes, the bony plates found along the lateral line of many other jack species, giving them a smoother feel.
- Their small, downturned mouth is perfectly adapted for sifting through sand to find buried crustaceans and mollusks.
- Juvenile pompano often utilize estuaries and shallow surf zones as critical nursery habitats, providing them with food and protection.
- They undertake seasonal migrations, moving north in warmer months and south as temperatures drop.
- Pompano are schooling fish, often found in groups, which can offer some protection from predators.
- The species has significant potential for aquaculture, with ongoing research into sustainable farming practices.
- Their diet primarily consists of sand fleas, coquina clams, and various small crustaceans, making them important regulators of these invertebrate populations.
Conclusion: A Treasure of the Tides
The Florida Pompano, with its sleek form, spirited nature, and vital ecological role, is truly a treasure of our coastal waters. From its intricate dance within the food web to its cherished place in human culture, this fish exemplifies the rich biodiversity of marine environments. Understanding and appreciating the Florida Pompano not only enriches our knowledge of the natural world but also underscores the importance of conserving the delicate ecosystems it calls home. Whether you encounter it on a plate, at the end of a fishing line, or darting through the surf, the pompano is a reminder of the ocean’s enduring wonder.

![Red Angus Closeup of a beautiful Red Angus cowPhoto by: U.S. Department of Agriculture [pubic domain]https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/](https://animals.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/Red-Angus-4-238x178.jpg)




![Red Angus Closeup of a beautiful Red Angus cowPhoto by: U.S. Department of Agriculture [pubic domain]https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/](https://animals.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/Red-Angus-4-100x75.jpg)

